Atrial fibrillation (Afib) carries a heavy clinical burden, with patients experiencing a 5x greater risk of stroke1 and a 5x increase in heart failure.2 These patients also experience up to a 47% reduction in quality of life related to anxiety about medications and burnout from frequent doctor appointments.3-9
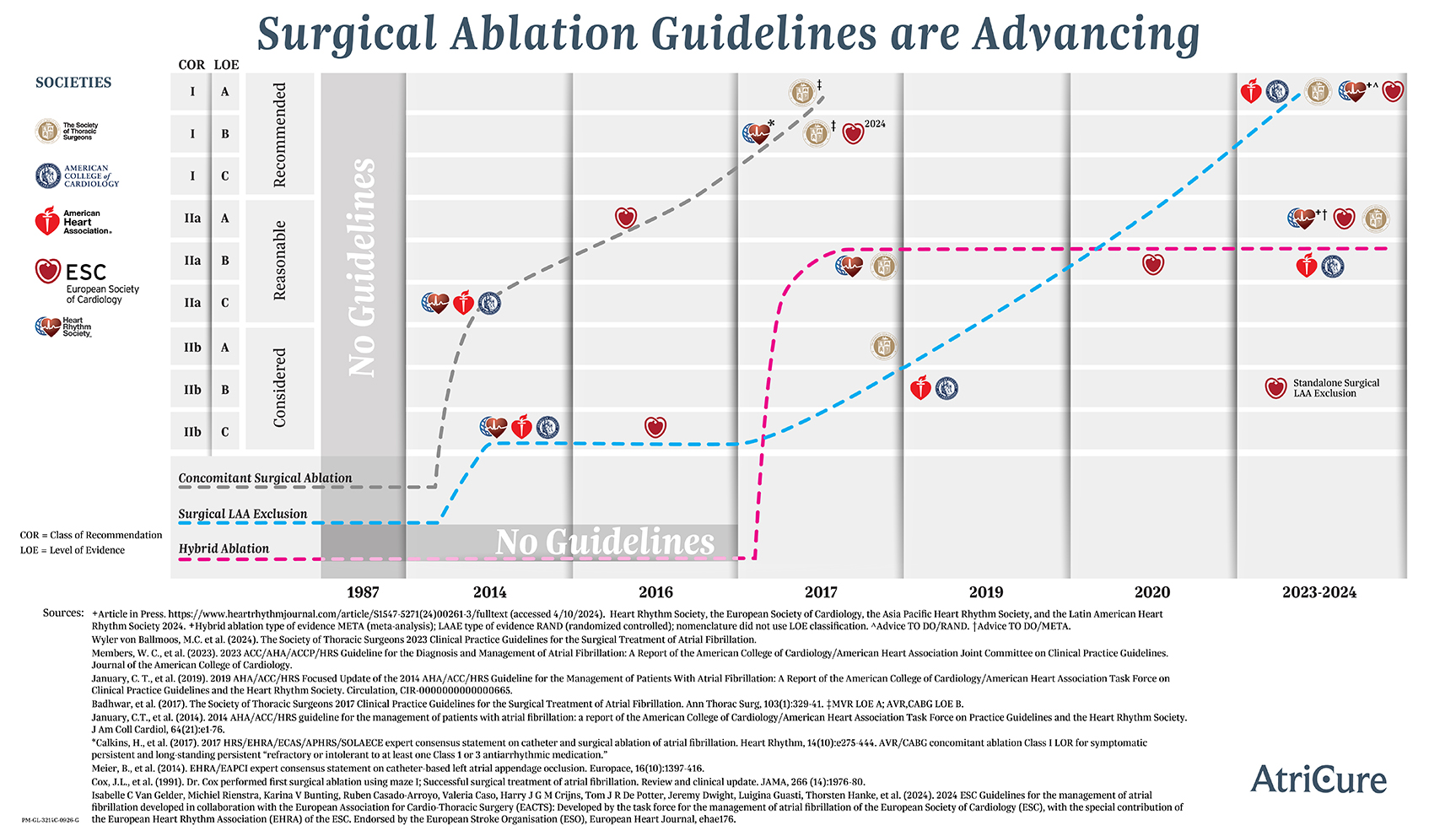
For patients with Afib needing open heart surgery to fix a coronary or valve issue, the Society of Thoracic Surgeons recommends performing surgical ablation (Cox-Maze procedure) at the same time, giving it their highest level of recommendation—Class I.10 Radiofrequency energy is the primary means to create surgical ablation lesions.
AtriCure has a robust lineup of clamps, pens and probes that can be used for ablating cardiac tissue with either cryothermia or bipolar radiofrequency energy. Several AtriCure pens also have the ability to pace, sense, and stimulate.
Patient Spotlight
Meet Dorsey, a passionate music store owner who knows the importance of a steady beat. Faced with aortic valve disease, coronary disease, and Afib, his doctor, Dr. Robert Farivar, recommended addressing all three at once. After surgery, including LAA exclusion, Dorsey’s heart is back in rhythm—allowing him to get back to what he loves most.
Watch his story to learn more about the importance of putting patients back in normal sinus rhythm.
- Fukunaga et al. (2008) Fukunaga S, Hori H, Ueda T, Takagi K, Tayama E, Aoyagi S. Effect of surgery for atrial fibrillation associated with mitral valve disease. The Annals of Thoracic Surgery. 2008;86(4):1212–1217.
- Boriani G, Proietti M (2017) Atrial fibrillation prevention: an appraisal of current evidence. Heart (0):1–6
- Nazli C, Kahya Eren N, Yakar Tuluce S, Kocagra Yagiz IG, Kilicaslan B et al. (2016) Impaired quality of life in patients with intermittent atrial fibrillation. Anatol J Cardiol 16 (4): 250-255.
- Thrall G, Lane D, Carroll D, Lip GY (2006) Quality of life in patients with atrial fibrillation: a systematic review. Am J Med 119 (5): 448.e441-419.
- Hagens VE, Ranchor AV, Van Sonderen E, Bosker HA, Kamp O et al. (2004) Effect of rate or rhythm control on quality of life in persistent atrial fibrillation. Results from the Rate Control Versus Electrical Cardioversion (RACE) Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 43 (2): 241-247.
- Hoegh V, Lundbye-Christensen S, Delmar C, Frederiksen K, Riahi S et al. (2016) Association between the diagnosis of atrial fibrillation and aspects of health status: a Danish cross-sectional study. Scand J Caring Sci 30 (3): 507-517.
- Dorian P, Jung W, Newman D, Paquette M, Wood K et al. (2000) The impairment of health-related quality of life in patients with intermittent atrial fibrillation: implications for the assessment of investigational therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol 36 (4): 1303-1309.
- Centers for Disease Control Atrial Fibrillation Fact Sheet. https://www.cdc.gov/dhdsp/data_statistics/fact_sheets/fs_atrial_fibrillation.htm. Accessed Dec 2018.
- Annals of Emerg Med, 2008 Jan;51(1): 58-65, Epub 2007, April 27
- Badhwar, V. et al. (2017). The Society of Thoracic Surgeons 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Surgical Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation. Ann of Thorac Surg, 103(1):329-41.